
Implementing information technology in any organization presents a variety of challenges to any management. Universally, 30-60% of information technology implementations fail – with healthcare and elderly care being on the higher side of this spectrum, resulting in hundreds of millions of dollars in losses, litigations and opportunity cost of lost time consequently leaving both parties frustrated.
The healthcare industry, specifically the elderly care industry has garnered a lot of attention as the Covid-19 pandemic hit the world early 2020, resulting in over 500,000 of infections and 27,000 fatalities, and fatality rates in the 60+ estimated at over 20%. Not only did it widely expose the inefficiencies and gaps in healthcare and care delivery system worldwide, but it also divulged the serious deficiencies in the elderly care system.
Today there are close to 50 million people, 65 and over in the US. By 2060, this number will exceed 98 million – nearly a
fourth of the population, thanks to higher fertility rates, lower mortality,
and increased migration from poor and war-torn nations to these stable
countries. The global population of individuals aged 80 and over is likely
to triple during that same timeframe, from 143 million to 426 million. Moreover, in the
United States, 65+ elderly which constitutes 13% of US Total population, consume
more than more than 50% of care dollars annually. People aged 85+ cause 25% of
hospital readmissions incurring billions
of dollars of avoidable expenditure and consequently taxing our impoverished healthcare
system.
Healthcare is on the brink of digital revolution
The world of healthcare is on the brink of a
digital revolution that promises to transform the way care is delivered and consumed across the entire spectrum of
services. Innovative cloud-based technologies, digital interfaces and
patient-friendly digital tools powered by advancements in artificial
intelligence are making it easier for providers of all kinds to provide cutting
edge, patient centered care.
Elderly care is the fastest growing segment of the global healthcare market. Yet, paradoxically, technology adoption in many elderly care organizations continues to lag far behind the norm. Face-off between technology budget allocation to support clinical applications and technology for operational applications is very common, with technology for operational applications often having to bow out in favor of technology for clinical applications.
Many elderly care facilities resort to investing in a substantial amount of manpower for supervising residents’ daily activities as a catchall and an easy go-to, quick-fix solution. This is an imprudent allocation of budget. The high cost of labor is unjustified and does not yield compelling or proven advancements in care quality or business efficacy.
Residential facilities like assisted living centers and nursing homes occupy a unique healthcare niche, in which medical and hospitality services overlap. Although these elderly care facilities operate at the intersection of several different aspects of healthcare delivery, they also serve first and foremost as home to those residents. As a result, along with providing a wide range of medical support services, residential facilities also need to operate like a well-managed resort or hotel, while providing the familiarity, comfort and ambience of a home.
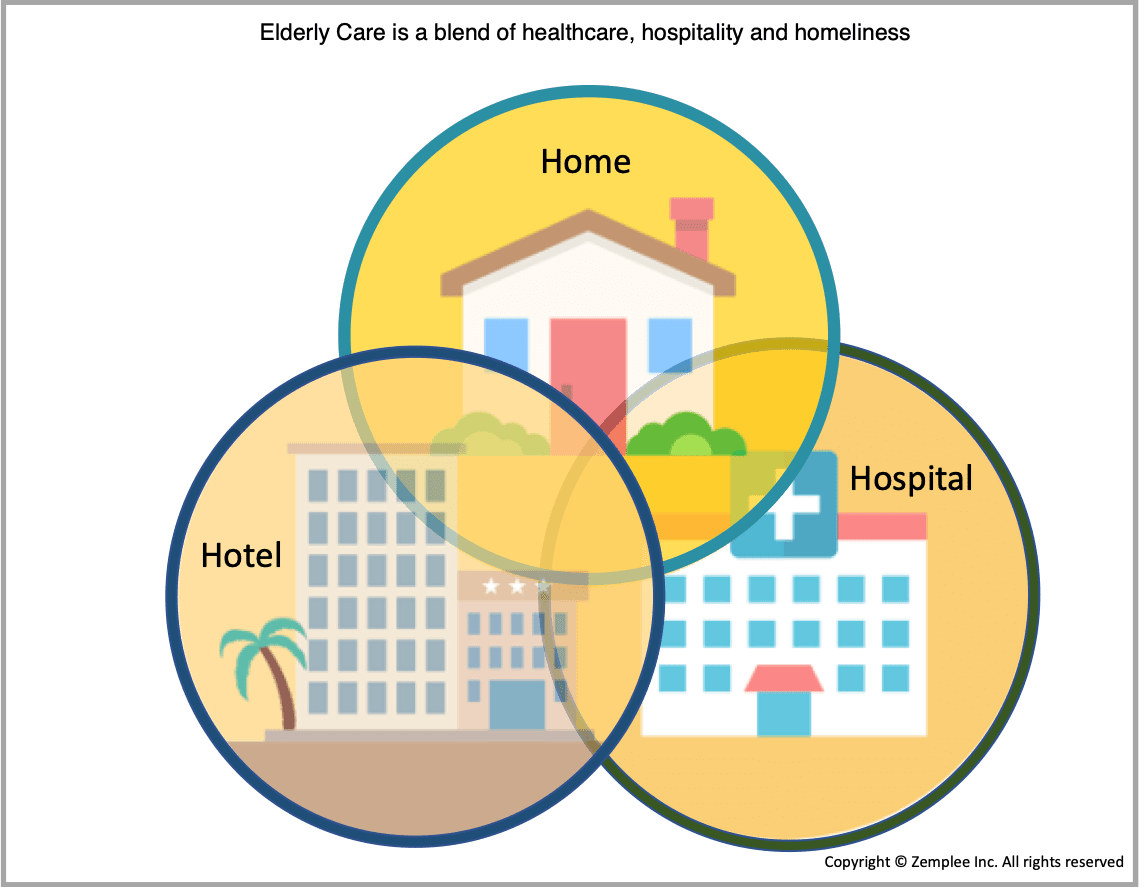
The increased demand for services ranging from managing chronic conditions to a complete set of nursing home care activities will test the limits of any existing system in an elderly care facility. Typical functions include managing resident records, billings, care plans and treatments as well as for providing a comfortable, well-appointed living spaces and enrichment activities for people with diverse needs.
Providers are increasingly challenged, because of severe caregiver shortage in the market. Inability to hire and staff their facilities and inevitability of adhering to regulatory requirements often requires them to operate at low occupancy rates which hurts business.
For these reasons, nursing homes, assisted living facilities and other types of services for elders need to rapidly adapt and reap the benefits of digital transformation. Digitization and automation platforms that can support technologies like telemedicine portals, wearable monitors and AI powered treatment protocols can help residential facilities provide more comprehensive, resident centered care and drive business growth.
Elderly Care: Digitization and Connected Care
We’re now living in the age of the Internet of Things, in which millions of devices ranging from phones to
“smart” cars, refrigerators and even entire city infrastructures can be in
constant communication. That’s made possible by advances in cloud-based
computing, which allows people to access information and do many other
activities at any time, from anywhere, on devices of all kinds. Along with
this, innovations in machine learning allow those devices to make decisions and
initiate processes, often without the need for any human input at all.
This new digital world has
profound implications for elderly care providers. Cloud based data
management allows doctors and caregivers to access patient information in
seconds. Telemedicine portals and wearable devices let patients manage many
aspects of their own care and share information with their provider team at, track
progress around the clock and provide on the spot recommendations. Artificial
intelligence can deliver preemptive care and with the power of data, predict
and prescribe and aid in proactive management of care or the business of care.
A growing number of people over 65 are using digital devices and apps to manage health
conditions such as diabetes, COPD and heart disease. As technology evolves and
gets smarter, DIY management of health will become mainstream and will advocate
an environment where fast access to needed information from any place, at any
time becomes essential and connected care ubiquitous.
Out with the Old and In with the New

For elderly care providers, assisted living facilities and nursing homes, making the shift from existing systems to a fully digital platform and implementing technology, a systematic program and planned approach to adaptation is important.
An often-overlooked fact is that any elderly care technology implementation is first and foremost, a quest for change management. Change is hard. It is underscored with fear and uncertainties. It demands organizational behavior change, cultural transformation, alterations in operating principles and modifications of policies and procedures. Additionally, Technology implementations, also have to factor in the organization’s ability to learn and adapt to new technology. Unless the right approach to change management is applied and the appropriate stakeholders are involved, it is almost impossible to have successful outcomes.
Shifting from a “legacy system” that includes monolithic, siloed computer systems and nd time-consuming manual routines to an integrated, cloud based digital platform can make it easier to offer coordinated, patient centered care in a variety of settings.
Many existing facilities aren’t prepared to integrate new technologies into their daily procedures, which limits their ability to meet demand for high-quality services. Consequently, this also makes it harder for elderly care providers to compete with more advanced care models. Only facilities leveraging the power of technology will be in better positioned to compete in this space. Not only that, eldercare providers have to step up to be a better ecosystem partner and players. The elder care industry must collaborate and coordinate services with many other healthcare entities including hospitals, primary care physicians, and direct care staff and most importantly the families that are the most important stakeholders. Connecting these disperse dots is extremely crucial to scaling the quality of care and delivering the highest level of love, care and comfort for our elderly, as they live through their twilight years.
Here are 8 essential steps elderly care providers need to know about implementing information technology
- Comprehensive Needs Assessment
- Education
- Research
- Budget
- Evaluation and Selection
- Implementation Approach
- Deployment, Orientation and Training
- Post Installation Evaluation
Over the next
few weeks, we will cover more details on each of these topics and offer you
some tools and templates to help you with your digital transformation mission.


